Buying A Web Business |
The Buying Process |
Doing The Deal |
Why buy a website?
The main objection I see raised about buying websites is why pay all this money for a website when I can just start one from scratch? Here are some reasons that you would buy a website:
It’s a good investment
The internet isn’t going away any time soon. The Global Financial Crisis caused millions to lose a lot of money. Getting 3-7% on real estate and 10% on stocks isn’t that attractive. Why not try a new asset class getting 40-100% return on investment.
Gain Time
Buying a website lets you fast track the time it has taken the founders to develop a website. There is a certain amount of lead time you must endure before getting traction with any new business. Acquiring a website eliminates this process and allows you to leap frog years of hard work.
Make profit from day 1
There is a certain lag time for a new business where you build up momentum. By purchasing an established website you start making money from day 1.
Growing industry
We are just at the infancy of the web. With anything the earlier you invest in a growing industry the more money you make in the long term.
You can always resell
All things being equal, if you buy an established website and make no changes you can probably sell it for around the same money that you bought it for.
Easier to obtain finance
A proven track record will make it easier to get financing from an external source or from the seller.
Acquire Customers
When you purchase a website, you also acquire its customer base, whether that is actual customers (sales) or eyeballs(visitors).
Eliminate Competition
Buying your competitor means one less company to compete against.
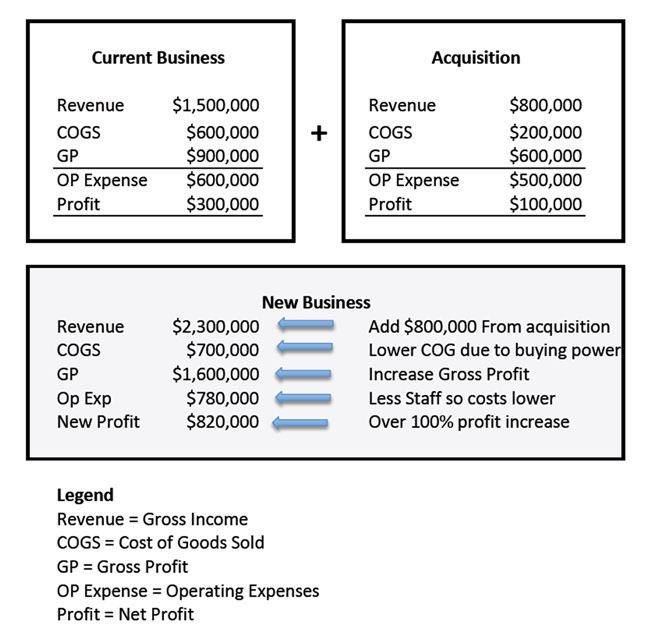
Employ Arbitrage Value
The following diagram represents the benefits you may achieve from arbitrage value. By combining two companies you can achieve some levels of synergy regarding revenue and expenses thus increasing the profitability of each business as one unit compared to separatly.
Increase Market Share
By acquiring a website in your market, you increase the size of your market share. You will find in most mature markets, there are only a handful of competitors (for example supermarkets). This is because, over time, markets consolidate.
Inherit Staff
Google is the master of this. With a limited pool of talented employees, it is sometimes easier to acquire a whole company to gain staff than to individually poach them from their existing workplace.
Increase Profits
Simply, if you have a business making $500,000 in net profit per year and add a business that is making $250,000 net profit per year, all things being equal, you will have a business that is making $750,000 per year. Nothing is ever as simple as that, but an acquisition should lead to an immediate increase in the bottom line if handled correctly.
What types of websites can I buy?
1. Advertising Sites
– these can either be blogs or static websites. They are either niche content or can be broad category sites like business. They are monetized through either pay per impression ads, pay per click ads, affiliate promotions or direct advertising. Examples:
- Large – www.cracked.com
- Medium – www.golf-newz.com
- Small – www.superweddings.com
2. Service Sites
– these sites offer a service to customers for a fee. They can either be one off or recurring. Example:
- Large – www.hostgator.com
- Medium – www.99designs.com
- Small – www.logodesignteam.com
3. Product Sites
– the oldest online business model. Takes a tangible product and sells it online. Example:
- Large – www.amazon.com
- Medium – www.cufflinks.com
- Small – www.theportablebarcompany.com
4. Subscription Sites
– driven by a paid membership or a subscription. Examples being a magazine, newsletter, club, application, Example:
- Large – www.readersdigest.com
- Medium – www.lynda.com
- Small – www.fastwebformula.com
5. Lead Generation Sites
– Lead generation combines advertising in a service model to generate “leads” or potential customers for that company and getting paid to do so. Examples:
- Large – www.creditcards.com
- Medium – www.dui.com
- Small – www.idahocarinsurancepros.com
6. Software
– a program created for a computer. The product can be charged as a one off or recurring. Examples:
- Large – www.salesforce.com
- Medium – www.basecamphq.com
- Small – www.speeddash.com
7.Web Applications (apps)
– commonly refereed to as apps. Usually consisting of a game or fun application these digital products earn revenue when users purchase them online. Examples:
- Large – www.Farmville.com
- Medium – www.myfitnesspal.com
- Small – apps.facebook.com/justdrawme
8. Forums –
These can either be free or paid forums. Free forums generally are free to join and are monetized through advertising. Paid forums cost money to join and generally earn money through a monthly or yearly subscription. Examples:
- Large – www.gaiaonline.com
- Medium – www.webmasterworld.com
- Small – www.mustangforum.com
What will determine what you buy?
- Acquisition Size – usually measured with annual sales. However depending upon other considerations, employees, plant and equipment and other measures may become important
- Transaction Size – Determined by the gross dollar value of the purchase and corresponds to your companies financial strength and adherence for risk.
- Transaction Structure – Usually a combination of cash, seller financing, third-party debt, and/or the use of stock as part of the purchase price.
- Financial Strength of the Target – Is the target business profitable or not. Are you willing to take on their liabilities and have a management team in place to turn a business around.
- Business Status – Defined as start-up, development, growth or maturity. It may be an idea to consider the stage of your own business to that of the target. Understand the challenges differences in these stages present.
- Geographic Location – This adheres to your comfort levels with one or more remote facilities and their distance from your main location.
- Synergy – The advantages of combing the two businesses, where markets, services or products are compatible
Steps To Prepare For An Acquisition
Everyone online is looking for the quick fix. Well sorry but there is none. Finding a good site to buy takes time effort and hard work. Sure you can setup systems and process that is going to make it easier to find oppurtunities (I list some below) however it can take days/weeks/months even years to find a good deal. I read in an article about a media company owner that spent 9 years courting a particular company that they wanted to purchase. This involved checking in once every 6 months with a phone call, asking how business was going and just building that relationship. Then when the time came that he wanted to sell, guess who was the first perso that came to mind ? So get yourself prepared:
- Get your finances ready (lots of deals fall through because of financing issues and buyers not being able to move quick enough)
- Get in contact with brokers and outline your requirements in terms of what you are looking for.
- Alternatively pay someone to do all the research for you and filter deals based on your requirements. Blatant plug for our services, we act as a buyers agent to help you find good delas if you need help.
- Register for all the online marketplaces like flippa.com businessforsale.com, bizquest.com
- Understand you are going to need patience and look at a lot of deals before finding the right one.
What defines a quality website?
- Profit producing website
- Most likely older than 1 year
- That has consistent earnings
- That has stable traffic
- Positive growth trend
- Processes automated
- Defensible Market (a site on CD’s has little value today)
- Room for growth
- Strong brand
- Diversification (of revenue and traffic)
- USP (some type of unique asset)
- Key assets (like email list, premium domain, supplier contracts etc.)
- Legal Liabilities (you have none)
Where can I find a business to buy?
Website brokers:
- www.digitalexits.com
- flippingenterprises.com
- latonas.com
- quietlightbrokerage.com
- wesellyoursite.com
- websiteproperties.com
Marketplaces
- Flippa.com
- websitebroker.com
Business for sale websites:
- Businessesforsale.com
- BizQuest.com
- BizBuySell.com
- BusinessBroker.net
Other ideas
- Scroll through DMOZ listings looking for sites that haven’t been updated for some time.
- Pay for an ad in the above business for sale websites
- Run a PPC campaign and direct it to a sell your website landing page (see in detail below)
What is the buying process?
Coming soon
How Much Should I Pay?
Coming Soon
Pre Purchase Checklist?
Generally the first thing you will look for when looking at a website to buy is how quickly can you get you money back. The main reason your looking to buy a website in the first place is to make a profit, so that should be your driving motivation. There is then two schools of thought regarding the type of site you would want to buy 1. Undervalued site – normally a distressed seller or someone with a site that doesn’t understand the full potential of it 2. Strong investment – normally a site that has steady growth is most likely mature in it’s earnings and you are looking for a place to invest your money. When looking at sites to buy there will be a number of common questions that you will want to ask before you go into detailed due diligence.
Questions like:
- What is the gross revenue?
- What is the net profit?
- What are the expenses?
- What is the breakdown of traffic sources?
- How much time per week do you spend on the website (the owner)?
- How may staff manage the website, what are their roles?
Generally something that looks too good to be true is usually….too good to be true. A couple of other tips:
- Speak to the seller before buying
- Use an escrow service when transferring money
- Make sure you ask for the historical traffic and income data
Financing Options
No matter perfect you due diligence is you can’t predict the future. A more public example of creative financing. You may want to develop some sort of performance based payment scheme so you can decrease the risk by paying some money upfront and some money after certain milestones have been achieved. Here is a breakdown of payment structures you may want to adopt. There are three most commonly used financing strategies that you may employee when buying a website. Just a note most deals in the sub 100k range will not have an aspect of seller financing.
- Seller Financing– A website is sold for $200,000. $150,000 is paid upfront in cash and the remaining $50,000 is paid off over 12 months at 10% interest. So in the end the seller gets $205,000 for their website.
- Performance Based Financing– A website is sold for $200,000. If after a 12 month period the websites monthly income has been more than $18,000 for the past three months running, a bonus payment of $40,000 is to be paid. Example 2 – A website is purchased for $200,000 and the seller is entitled to 8% of gross profits for the website over the next twelve months.
- Holdback Financing – A website is sold for $200,000. $180,000 is paid upfront and $20,000 is paid after 30 days once the website seller has provided training to the new owner.
Due Dilligence Checklist
Due diligence is the research you conduct prior to buying a website. The process allows you to asses the risk of your investment as well as verify the claims made by the seller regarding the website.
Due diligence is the skill of uncovering facts and information that isn’t immediately apparent. This involves analysis of the data that is given to you by the seller but also checking third party data as well. By asking the right questions, digging just below the surface and drawing educated conclusions you will be able to uncover everything before purchasing. Purchase yourself this checklist or hire an expert to assist with the due diligence process.
I believe due diligence on websites should be broken down into three categories.
- Financial
- Legal
- Technical
Financial Due Diligence Checklist
- Bank Statements
- Merchant Facility statements
- Paypal account statements
- Third Party payments – ie Affiliate commisions, Ad Sales, Adsense, Amazon, Clickbank etc.
- Accountant prepared P&L’s
- Tax returns
- Costs of goods sold expense reports – invoices and wholesale pricing proof
- Supplier invoices – e.g. advertising, consulting
- Emplyee verification – payroll, tax returns
- Recalculating “real” net profit using add backs and add-ins (accounting modelling)
Technical due diligence checks:
- Traffic details – from server stats and preferably a third party statistics service like Google Analytics
- Database information – check supplier records, logins.
- Where the site has received a google penalty, look for a drop in traffic – www.semrush.com
- Download SEOquake for chrome or mozilla firefox and fo a quick check on the site stats – www.seoquake.com
- Check traffic for the sites keyword/keywords:
- Search for references on the domain in google and bing to see any mentions – www.domain.com, domain.com
- Check if the site is indexed in google – site:domain.com
- Check the backlink profile, select the tab referring domains to see if there is any sinister back links to the site – www.majesticseo.com
- Check the keyword traffic stats in adwords – https://adwords.google.com/select/KeywordToolExternal
- Use to see that sites lisdted on the ame IP address and that have the same adsense or analytics code – www.spyonweb.com
- Understanding the business model
- Check ballpark traffic stats for higher traffic sites – compete.com and quantcast.com
- Check Yahoo and DMOZ for a listing – dmoz.org and yahoo.com
- Check copyscape for duplicate content – www.copyscape.com
- Confirm the sites page rank, is it real or fake –pr checker
Legal due diligence checks:
- Domain registration details to verify ownership and registration dates
- Check Whois to do a second check on the ownership – www.whois.com
- What the site used to look like to check it the site used to be something more sinister – www.archive.org
- Trademark/Copyright records
- Background search on the company or LLC.
- Legal leans or lawsuit
- Supplier agreements
- Employee agreements
Legals
Coming soon.
Escrow
Generally most large deals will involve a third party who will handle the money transfer. In real estate deals it is usually a lawyer or real estate agent (realtor). In most internet deals it is a third party online service called escrow.com. The process works as follows:
- Buyer and seller agree on terms – the selling price
- Buyer pays escrow – the buyer transfers money from his bank account into the third party bank account
- Seller ships the merchandise – The seller will transfer the domain name and any assets (website, hosting account, content, payment processors, files, documents, email accounts etc.)
- Buyer accepts the marchandise – you will receive the domain and assets, you will then confirm with escrow.com that you have received the everything that has been agreed upon and instruct escrow.com to release the funds to the seller
- Escrow pays the seller – they will release the funds from their bank account to the sellers bank account